Physics > Waves > Electromagnetic spectrum
EM waves can have wavelenths that range from nanomenters to kilometers!
The electromagmetic (EM) spectrum consists of eletrocmagnretic waves of various frequencies (and wavelengths). As the frequency varies, their properties also vary a lot. The image below illustrates the whole spectrum:
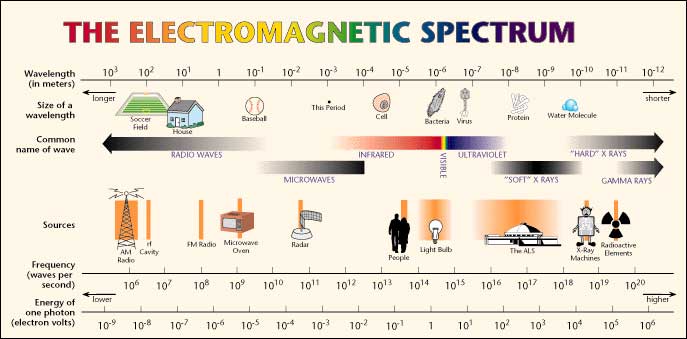
EM spectrum Credit: Wikipedia
Link to previous topics: Heat
We learnt that heat can be tranmsmitted by conduction, convection and radiation. The latter is the mode associated to EM waves.
All types of EM waves can transmit heat, although IR are the ones more frequently associated with heat. All bodies that are above the 0K tempereature emit IR waves, to some extent.
The hotter they are the more IR they emit. IR cameras are very useful for night vision and also to see hidden structures, like the heating elements below the floor of a house. Lots of interesting IR images can be seenl here.
IR is associated to global warming because it is the radiation that is trapped in the planet. It cannot escape because it is reflected back mby some types of molecules that are part of the atmophere.
A lot of the heat that is radiated by the Sun is in the from of microwaves, but not all. Some of the heat is also trasnsmitted by other types of EM waves, especially light and UV. Light carries a lot of heat from the Sun, which is cleverly exploited in solar power plant loke this one. UV also carries a lot of heat, and it is the frequency responsible for sunburns,
Even radiowaves can cause burns, if they are powerful enough. At the opposite side of the spectrum we have gamma rays, which is the most energetic radiation odf the whole spectrum. Those cause serious burns, such as thopese observed in survivors of nuclear disasters . Sometimes people involved in nuclear accidents get the skin brown, due to the radiation received, what is usually called a "nuclear tan". People that undergo radiation therapy to kill cancer cells get localized radiation burns..
Finally, I need to mention microwaves which are also capable of causing heating, as in the microwaves oven.
Conventional x microwave oven
In certain electric ovens mosat of the heat is carried by IR radiation (reference gere). How does thgis cimpare with a microwave oven?
The microwaves used in ovesn , with freqwuencies of 2,5 GHZ, interact with water molecules (which are very polar) causing htrem to rotatae. This rotations cause attrition among neighbouring molecules, which causes heating.
It is intersting that tgis particular frequency interac only with water so that other materials in the oven don´t get hot. Those include the air, the oven walls, plates and even parts of the food that are too dry.This is an advantage becaise energy is spent only on what needs to be heated. Another advantage of microwave heating is that they are more penetratiing than IR, so thjat they cause heating deep inside the food. IR, in contrast, only heats the surface of the food; the heat moves from the surface to the interior by conduction, which is a slow process. That is why it may happen that the outside of the food gets burned while the interior is still uncooked.
The microwaves don´t have the same intensity in all positions inside the oven and that is why the food needs to be rotating, to average the energy received at different spots. The hotspots in a microwaves oven can be located by purirng rows of marshmallows (without the rotating p´late) and checking which ines raise the most.
Mind you that it is important that ythe walls of the ovne are in good condition to stop leakeage of microwaves, which could burn people on the proximity. This possibility has been explored for the military, which makes use of a thermal weapon based on microwaves. It is called acitve denial system.
